每日一言
At this point, no matter how I change, the things I’ve lost won’t come back. — Yuuji Kazami from The Fruit of Grisaia
在Flask框架的使用一节中已经介绍了路由的大致用法,这篇文章我们详细学习一下flask框架中路由使用的更详细的规则。
定义路由
定义一个最基本的路由格式如下:
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return "This is the index";
对于一个Flask应用,用路径 / 代表根目录,也就是我们直接访问URL所访问的页面。
@app.route('/')被称作修饰器,用于将路由于对应的视图函数进行绑定。修饰器后必须紧跟一个函数,否则会报错。def index():视图函数
路由参数
flask可以捕获Client端访问的URL中的部分内容作为参数,进而传递给视图函数。
@app.route('/greet/<name>')
def greet(name):
return f'Hello, {name}!'当Client访问URL:/greet/LiHua 时,视图函数会返回:“Hello LiHua”
请求方法
Flask 路由支持不同的 HTTP 请求方法,如 GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等。可以通过 methods 参数指定允许的请求方法。
@app.route('/submit', methods=['POST'])
def submit():
return 'Form submitted!'methods参数是一个数组,可以选择多种指定的方法允许访问。
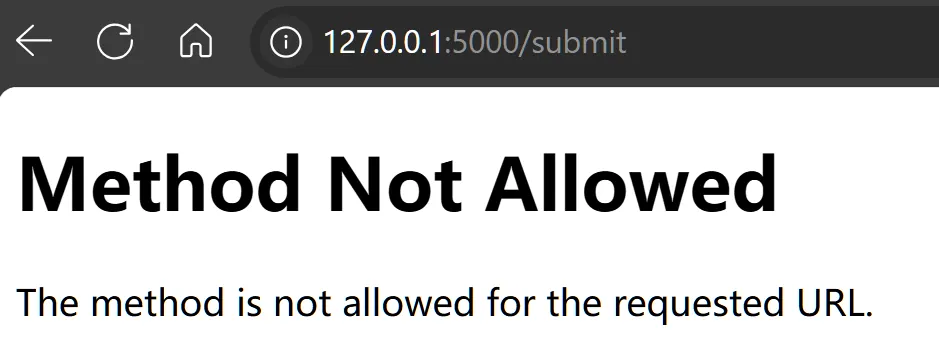
如对于设置为只能通过 POST方法请求的路由,我们通过浏览器直接进行get访问就会报错:Method not allowed
路由优先级
Flask 按照定义的顺序匹配路由,第一个匹配成功的路由将被处理。确保更具体的路由放在更一般的路由之前。
@app.route('/user/<int:user_id>')
def user_profile(user_id):
return f'User ID: {user_id}'
@app.route('/user')
def user_list():
return 'User List'视图函数的其他修饰器
除了路由修饰器 @app.route()外,视图函数还有三个其他的修饰器:
@app.befor_request:在每个请求处理之前运行的函数。@app.after_request:在每个请求处理之后运行的函数。@app.teardown_request:在请求结束后运行的函数,用于清理工作。
对于有以下一组修饰器的Flask程序来说:
@app.route('/')
def index():
print("request received")
return "This is the index";
@app.before_request
def before_request():
print('Before request')
@app.after_request
def after_request(response):
print('After request')
return response
@app.teardown_request
def teardown_request(exception):
print('Teardown request')程序运行结果为: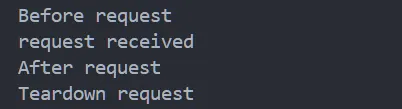
我们可以知道四个路由的调用先后顺序为:before_request->route->after_request->teardown_request