每日一言
Obeying a superior you can’t even believe doesn’t make you loyal. You’re just fooling yourself. — Olivier Mira Armstrong from Fullmetal Alchemist: Brotherhood
三、简答题
-

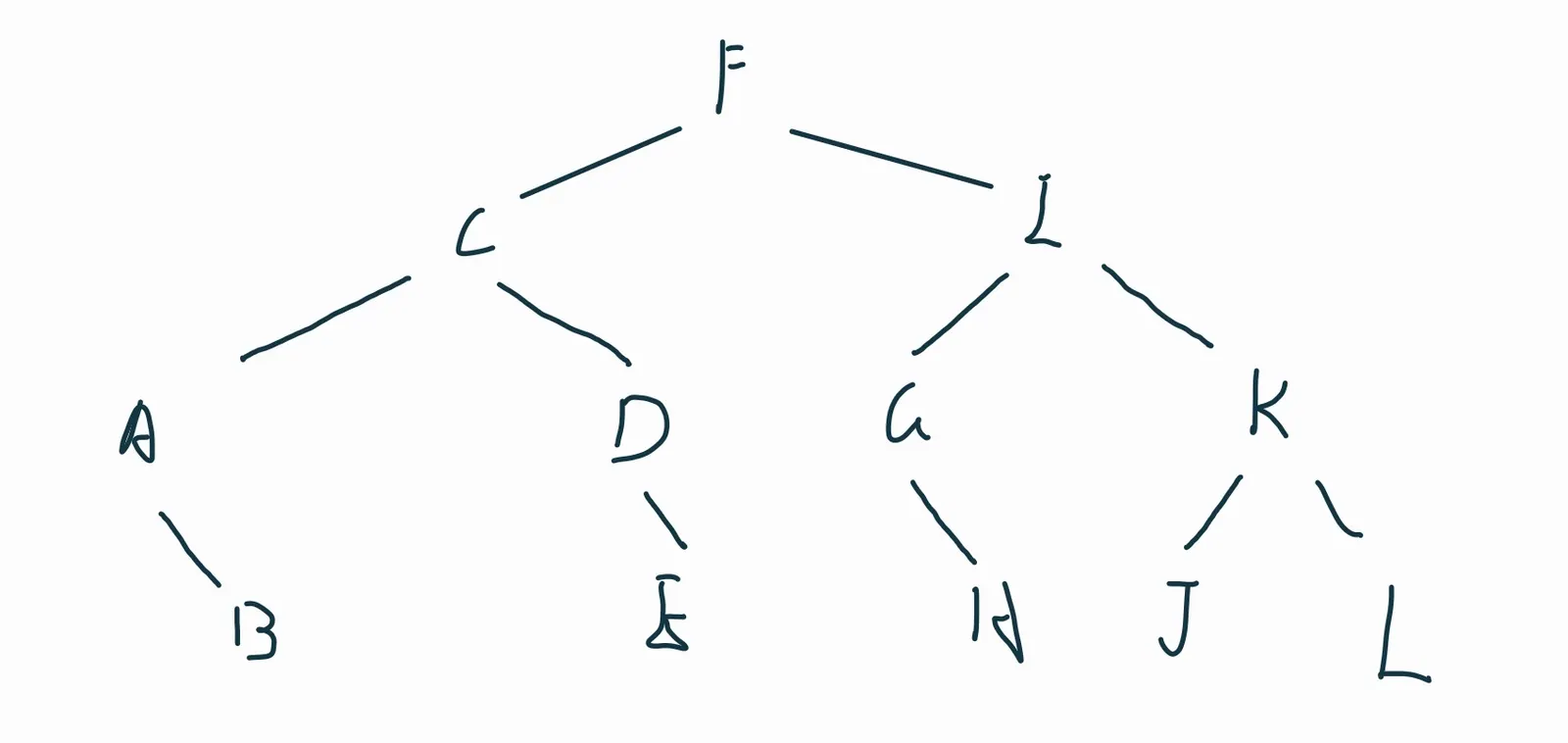
12个字符串的字典序为:Apr、Aug、Dec、Feb、Jan、July、June、Mar、May、Nov、Oct、Sep
-

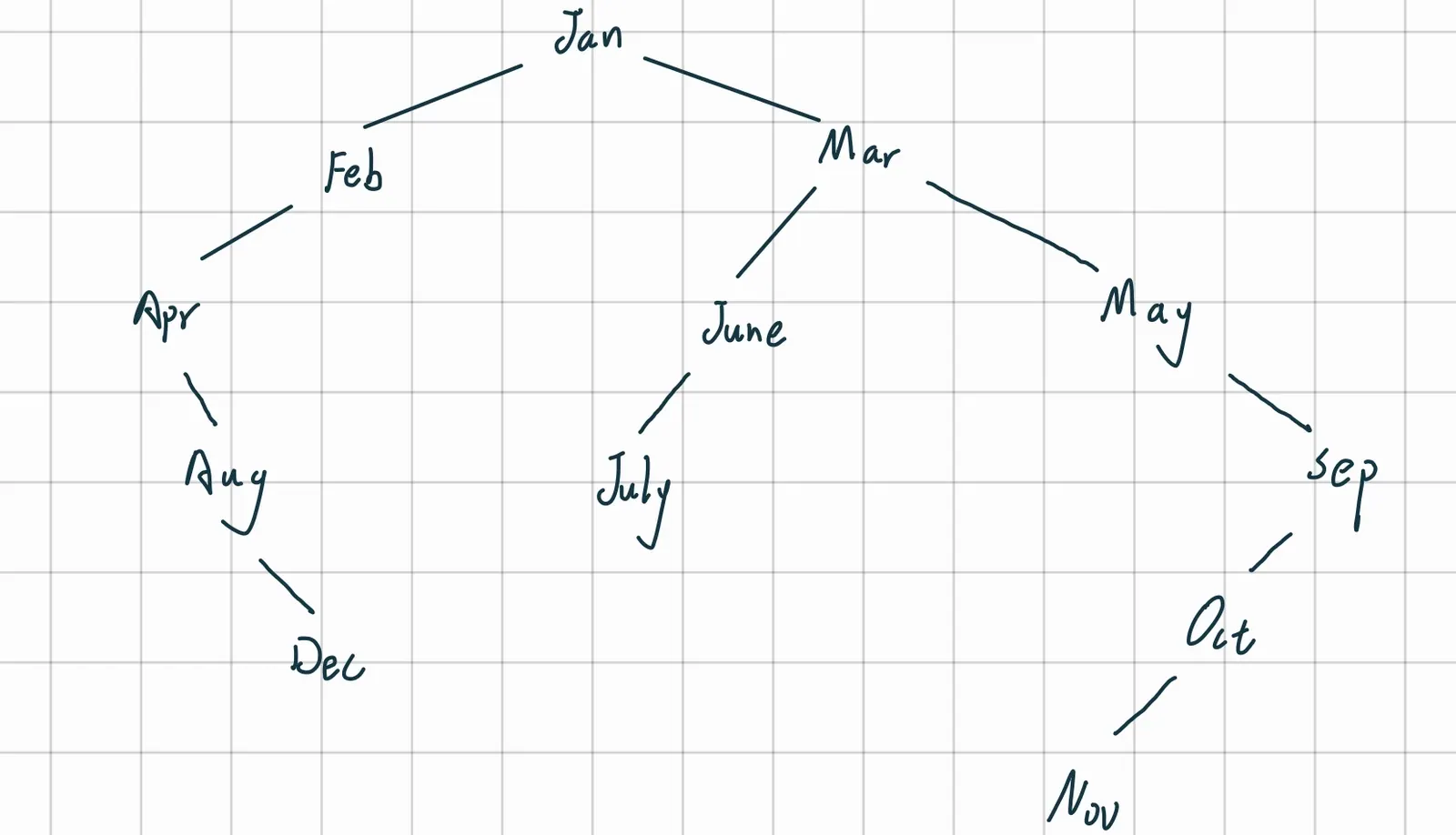
对于三阶B-树,每一个结点最多有2个key值,三个子树。
插入前两个key值:

插入50时有溢出,需要分裂:
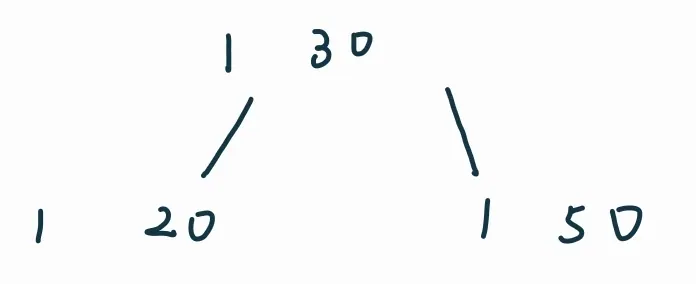
插入52:
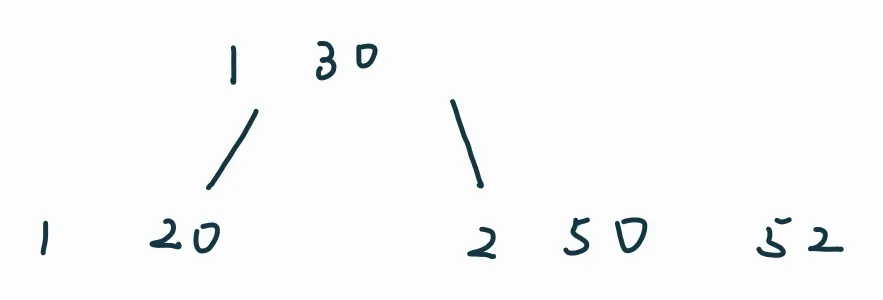
插入:60
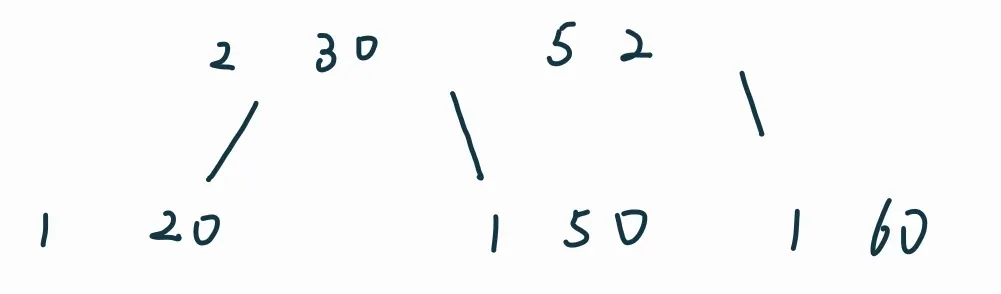
插入:68
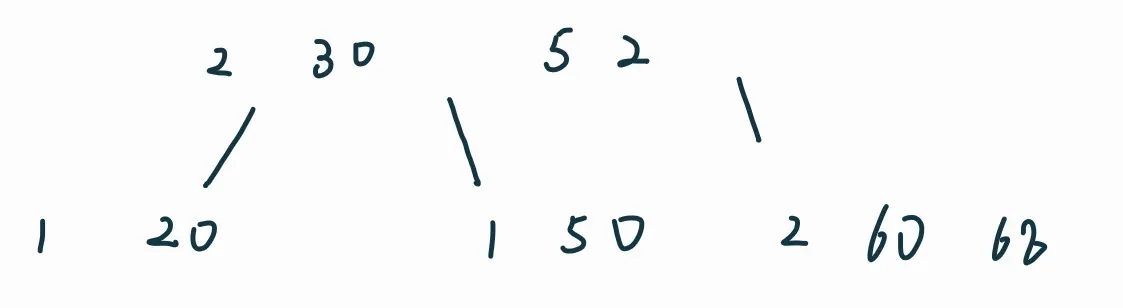
插入70:
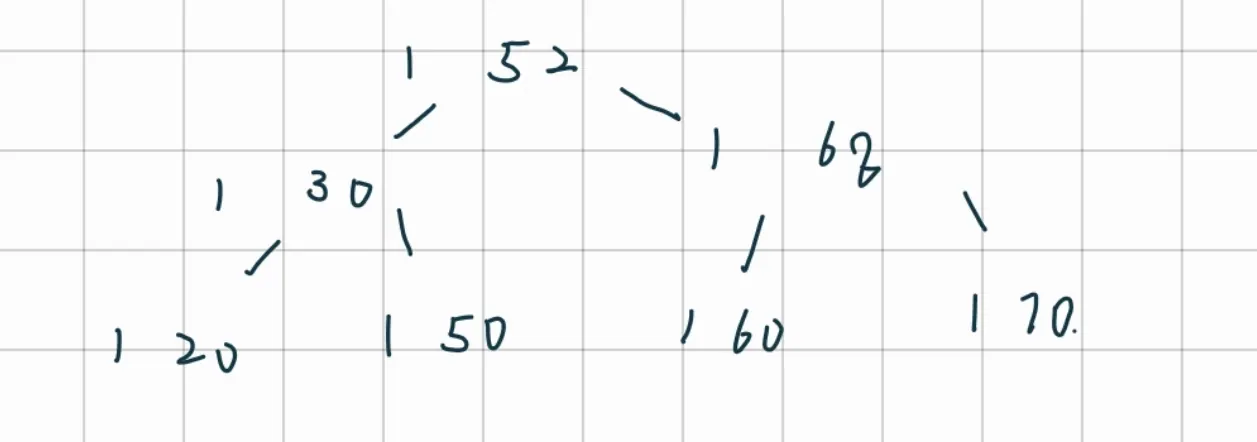
删除50:
-
合并
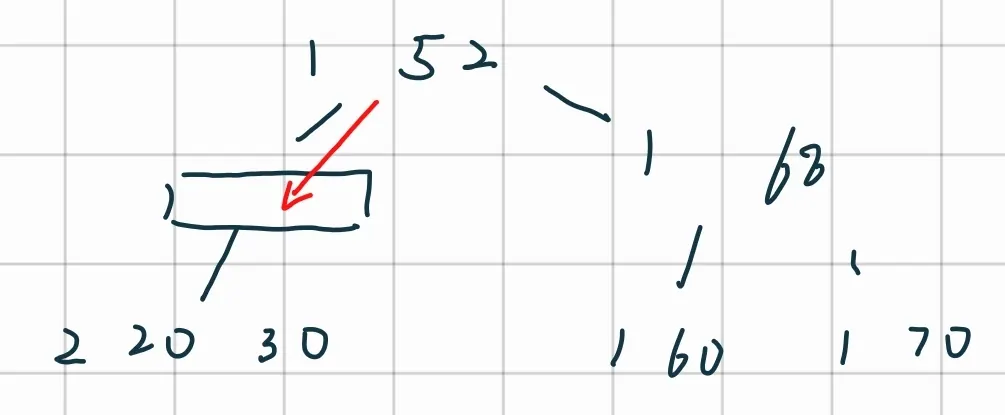
-
再次合并
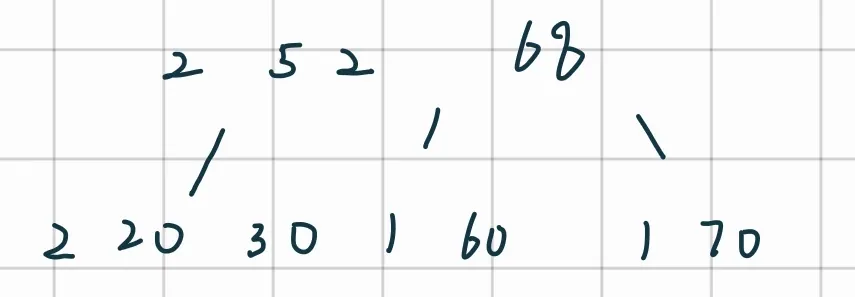
删除68:
-
交换:
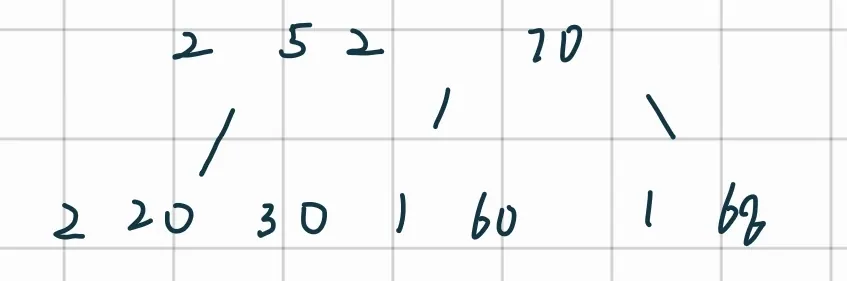
-
删除
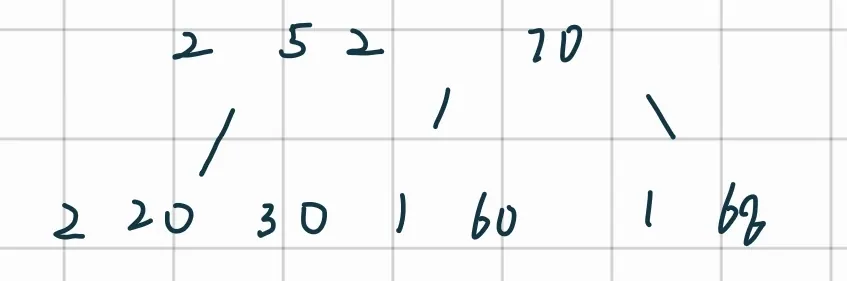
-
合并:

-
-

构造哈希表:22%11 = 0 , 41%11 = 8, 53%11 = 9, 46%11 = 2, 30%11 = 8, 13%11 = 2, 1%11 = 1, 67%11 = 1.
-
线性探测开放定址法
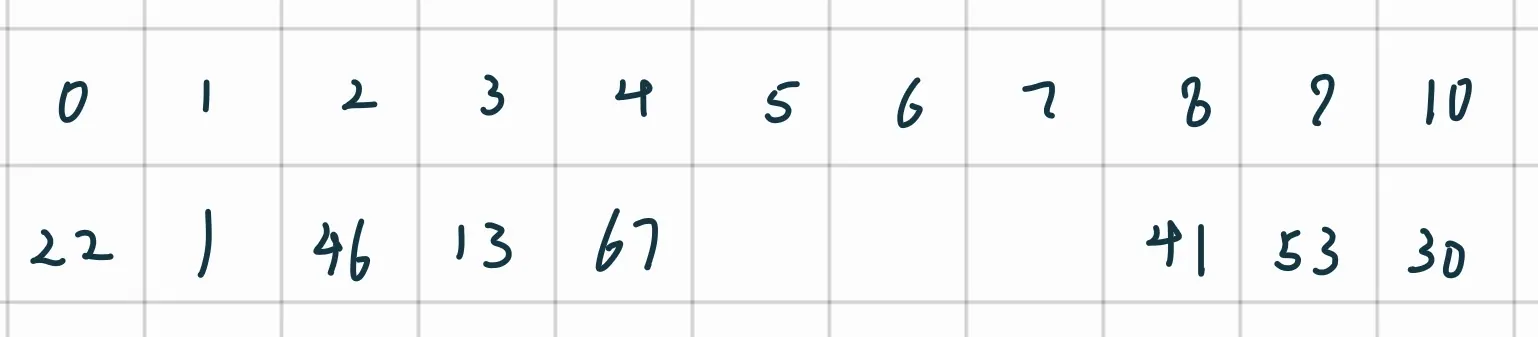
成功时:
失败时:
填装因子:
-
链地址法
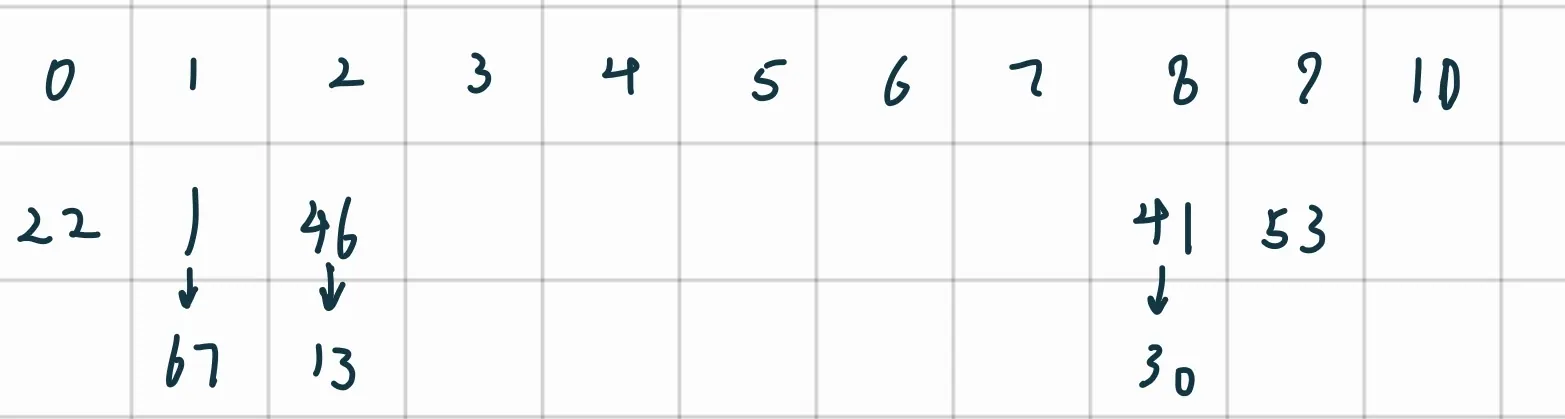
成功时:
失败时:
填装因子:
-
四、算法设计题
-
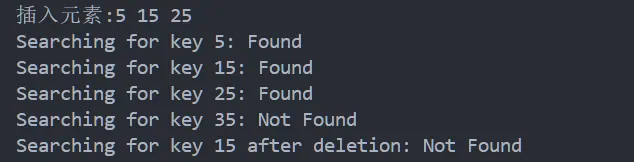
查找序列以带头结点的单链表表示,各结点中除了关键字外还有设有一个此关键字的访问次数计数值,初始值为0(假设计数值可以很大不会向上溢出),每次查找成功后该结点访问次数计数值加1;当本次查询结束后,将查询成功的结点向前调整到合适位置保持在单链表中访问次数计数值是从大到小排序的。
试给出时间复杂度为O(n)的查询算法实现,函数名、参数、返回值请自行定义。
代码如下:
typedef struct Node{
int key;
int read_count = 0;
struct Node* next;
}Node;
bool search(Node* head,Node* parent,int v)
{
bool j = true;
if(head->next == nullptr)//未找到
return false;
if(head->next->key == v)//找到
{
head->next->read_count++;
}
else
{
j = search(head->next,head,v);
}
if(j == false)
return false;
if(head->read_count == -1)
return true;
if(head->read_count < head->next->read_count)
{
Node* tmp = head->next->next;
parent->next = head->next;
head->next->next = head;
head->next = tmp;
}
return true;
}运行验证:
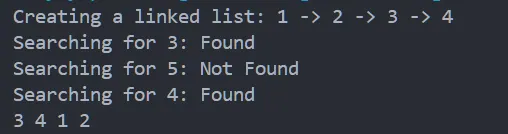
-
试给出判别一棵给定的二叉树是否是排序二叉树的算法,设二叉树以二叉链表表示。
函数名、参数、返回值请自行定义。
代码如下:
typedef struct data{
int type = 1;
int value;
}data;
typedef struct Bitree
{
data key;
struct Bitree* lchild,*rchild;
}Bitree,*Bitnode;
//返回值type == 1时为非空排序二叉树,type ==0 时为空树,type ==-1 时不是排序二叉树
data isBST(Bitnode T)
{
if(T==nullptr) return {0,0}; //空二叉树
else
{
data lc = isBST(T->lchild); //递归遍历左子树
data rc = isBST(T->rchild); //递归遍历右子树
if(lc.type == -1|| rc.type == -1)
{
return {-1,0};
}
else
{
if(lc.type ==1 && lc.value > T->key.value)
return {-1,0};
else if(rc.type ==1 &&T->key.value > rc.value)
return {-1,0};
}
return T->key;
}
} -
分别写出哈希表的初始化、插入关键词k、删除关键字k的算法,设哈希函数为H(假设哈希函数已经实现可以直接调用,参数和返回值请自行定义),解决冲突的方法为链地址法。
a) 哈希表的数据结构参考教材定义; b) 关键字类型为整数,需考虑空值的情况; c) 三个函数的函数参数和返回值自行定义。 哈希表以及结点定义如下:
typedef struct HashNode
{
int key;
struct HashNode *next;
}HashNode;
typedef struct HashTable
{
HashNode ** elem;
int count;
int sizeindex;
float a;
}HashTable;初始化函数如下:
bool InitHashTable(HashTable H,int sizeindex)
{
H.elem = new HashNode*[sizeindex]{nullptr};
H.count = 0;
H.a = 0;
H.sizeindex = sizeindex;
return true;
}插入函数如下:
bool Insert_Hash(HashTable H,int key)
{
int inx = Hash(key);
HashNode* new_key = new HashNode{key,nullptr};
if(H.elem[inx] == nullptr)
H.elem[inx] = new_key;
else
{
HashNode *p = H.elem[inx],*ap = p;
while(p != nullptr && p->key!= key)
{
ap = p;
p = p->next;
}
if(p == nullptr)
{
ap->next = new_key;//不存在,新插入
return true;
}
else
{
return true;//已经存在
}
}
return true;
}删除函数如下:
bool dalete_Hash(HashTable H,int key)
{
int inx = Hash(key);
if(H.elem[inx] == nullptr)
return true;//原本不存在
else
{
HashNode *p = H.elem[inx],*ap = p;
while(p != nullptr && p->key!= key)
{
ap = p;
p = p->next;
}
if(p == nullptr)//原本不存在
{
return true;
}
else//原本存在,删除掉
{
ap->next = ap->next->next;
delete p;
return true;
}
}
return true;
}运行验证: