操作系统期中习题复习
困死
简答题
2021-2022
1 . Please explain the principles of the multiple feedback queue secheduling algorithm.
系统按照进程类型设置多个独立的就绪队列,进程创建成功后插入对应类型的队列。每个队列中都有自己独立的进程调度算法。
队列间常用调度方式:
- 固定优先级:给队列之间确定固定的优先级,优先调度高优先级的队列。
- 时间片划分:给每个队列分配不同的时间片长度。
- Some atomic machine instructions support mutual exclusion(互斥) effectively. Define a procedure(程序) to make exclusion with instruction compare_and_swap for two boolean variable.
单词解释:
- Mutual Exclusion 互斥
- Atomic Instruction 原子指令
- Describe the priority inversion(优先级反转) problem in the realtime system(实时操作系统) with an example.
实时操作系统:对外部事件在有限时间间隔内做出及时响应的计算机/软件系统。
优先级反转:当高优先级任务需要访问一个被低优先级占用的共享资源时,如果低优先级任务在释放资源之前被长时间中断或延迟,就会导致优先级反转。
Example:当低优先级进程在持有互斥锁期间被高优先级进程抢占,高优先级进程随后尝试获取该锁时就会被阻塞。直到低优先级进程被重新调度并释放锁。
- Explain the implementation(实现)of conditional variables with “signal and continue“
conditional variables:条件变量
signal and continue 策略(Mesa/Hansen语义):在这种策略下,发出的信号量进程P唤醒进程Q后,进程P 会继续在管程内执行,直到它退出管程。或者自己再次等待。被唤醒的进程Q则被移至就绪队列。
signal and wait(Hoare语义):进程P唤醒进程Q后,进程P立即暂停执行。释放管程的控制权。等待Q执行完毕或Q再次等待。
2022-2023
- Define the states of a process(进程) and draw the complete static transition diagram for an operating system.
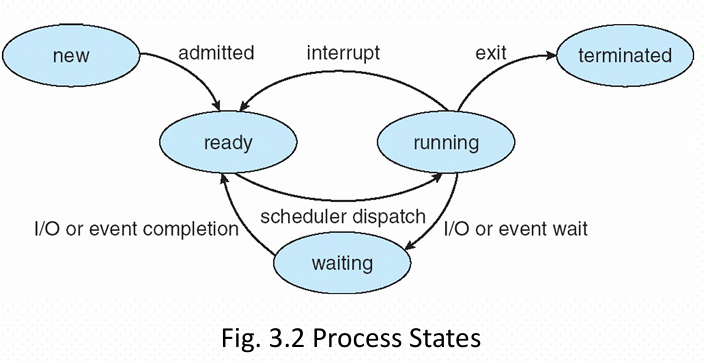
- Explain the priority inversion in real time system and give a solution to this problem
当低优先级的进程在持有互斥锁期间被高优先级进程抢占,高优先级进程会在尝试获取锁时被阻塞,直到等待低优先级进程被重新调度并释放资源。
- 死锁不考
- Explain the(Hoare) Signal and Wait semantics(语义) for the monitor implementations
当进程P唤醒进程Q后,进程P立即暂停执行并释放管程控制权。等待进程Q执行完毕或再次等待。
同步与互斥问题
1
here is a plate that can hold only one apple or can hold three oranges. Father put an apple once a time into the plate; mother put an orange once a time into the plate. If there is already one or two oranges on the plate, the mother can put another orange into the plate
Son takes an apple from the plate and eats. Daughter takes an orange from the plate once a time and eats.
The processes for the father, mother, son, and daughter are shown as followings. In order to synchronize these processes, please design semaphores and complete these processes by using wait() and signal() operations on semaphores.
a. Define semaphores needed and initialize them
分析题目同步与互斥关系:
同步关系:
- 父亲放苹果是儿子吃苹果的前驱事件
- 儿子消耗一个苹果产生空间是父亲线程的前驱事件
- 母亲放橘子是女儿吃橘子的前驱事件
- 女儿吃橘子产生空间是母亲放橘子的前驱事件
互斥关系:
- 所有线程需要互斥的访问盘子
数量关系:
- 盘子最多只能放一个苹果或三个橘子
模型梳理:
- 针对父亲与儿子、母亲与女儿是典型的生产者消费者模型
- 苹果与橘子之间关系类似于读者与写者模型。
定义需要的semaphores:
1 | |
定义的变量:
1 | |
b. write appropriate code segmentation for each place
1 | |
In a system with 2 processors, there are 10 concurrent processes sharing a type of resource based on a semaphore $S$, if each time,
(a) only one process is permitted to enter its critical section to use the resource, or
(b) at most 3 processes are allowed to enter their critical sections to use the resource,then answer the following questions.
(1). in these two cases, what are the initial , maximum, and minimum values for the semaphore S respectively(各自的).
a. 当只允许一个进程访问临界区代码时,信号量S取值为1。当没有线程申请进入时最大为1,当10个线程申请时最小为1-10 = -9;
b. 最多允许三个线程进入时S初始化为3,最大为3最小为10-3 = -7;
| Case | initial value | maximum value | minimum value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | 1 | 1 | -9 |
| (b) | 3 | 3 | -7 |
(2). what are the maximum, and minimum numbers of processes in ready, running, and waiting state.
注意考虑此题时已经和a,b情况无关
- ready:
- 最多可以8个进程ready,此时有两个进程在running
- 最少可以0个进程ready,其他进程可以在running也可以在waiting
- running:
- 最多只能2个
- 最少可以0个,此时所有进程都在waiting.
- waiting:
- 最多可以10个
- 最少可以0个,此时8个进程在ready,2个进程在running
| number of processes | ready | running | waiting |
|---|---|---|---|
| maximum | 8 | 2 | 10 |
| minimum | 0 | 0 | 0 |
2
In a kindergarten, the teacher distributed the fruits to children. All fruit would be placed on a large plate. The boys liked eating apples and the girls liked oranges. At the beginning, the plate was empty, which can contain 5 apples or oranges altogether. The teacher would put either an apple or two oranges into the plate each time. When she put an apple in the plate, a boy would get and eat it; and when she put two oranges in, a girl would get the two oranges and eat them.
(1). Please design appropriate semaphore-based processes to describe the behaviors of the teacher and boys and girls.
关系分析:
- 前驱关系:
- 老师放入1个苹果 -> 男学生吃一个苹果
- 老师放入2个橘子-> 女学生吃两个橘子
- 男学生取走一个苹果->释放一个盘子资源
- 女同学吃两个橘子->释放两个盘子资源
- 数量关系:
- 盘子容量为5
- 苹果和橘子可以混合放
- 苹果一次放一个,一次取一个
- 橘子一次放两个,一次取两个
- 互斥关系:
- 各线程互斥访问盘子
- 女生拿橘子这一动作应该互斥(参考哲学家就餐问题)
信号量创建:
1 | |
进程设计:
1 | |
(2). Make modificatons(修改) for the processes if a girl will get three oranges instead of two each time.
1 | |
(3). Can deadlock occur in your processes? Describe a scenario of deadlock if it can occur, or explain why deadlock cannot happen
在我的程序中不会发生死锁。我们详细分析一下生产者和消费者进程的等待条件:
老师进程:
- 当Splate <= 1时,可能阻塞。
男学生进程:
- Sapple <= 0时发生阻塞。
女学生进程:
- Sorange <=2时发生阻塞。
同时根据条件我们可以得到等式:Splate + Sorange + Sapple = 5
所以当生成者进程阻塞时:Sorange + Sapple >=4
消费者进程阻塞时:Sorange + Sapple <= 2
两个条件永远不可能同时成立,所以消费者进程与生产者进程之间不会相互等待发送死锁。